AI-Based Road Safety Audit Software



-
Identification of potential safety hazards or risks on the road
-
Recommendations for improvements to reduce the risk of accidents
-
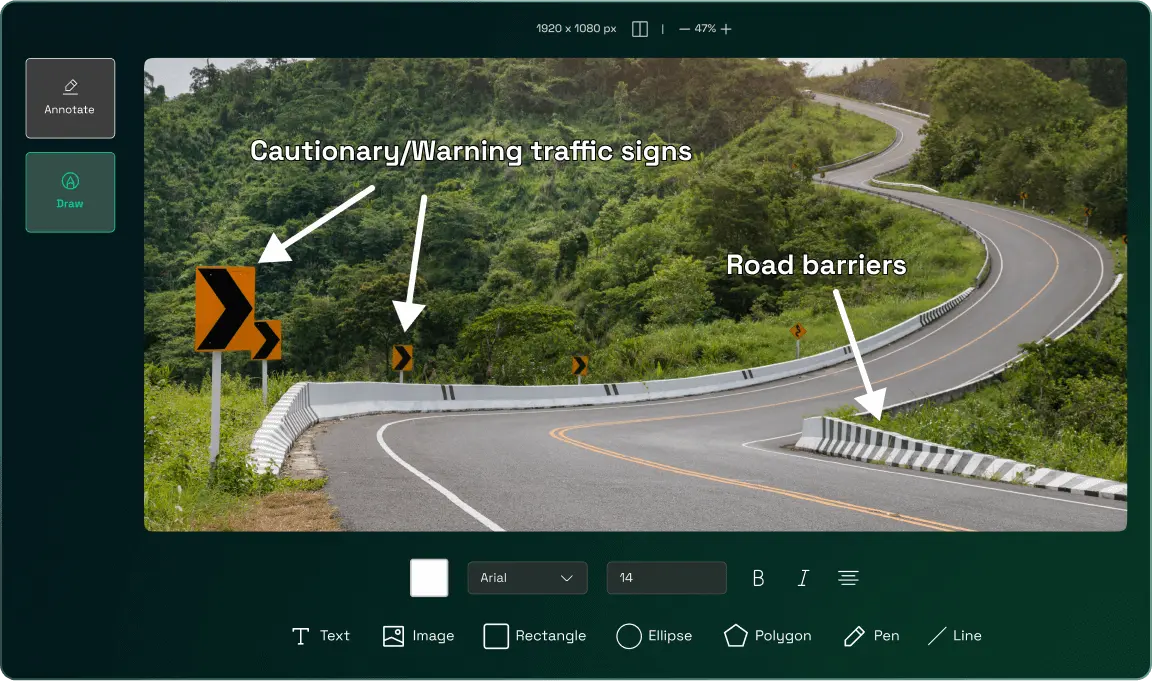
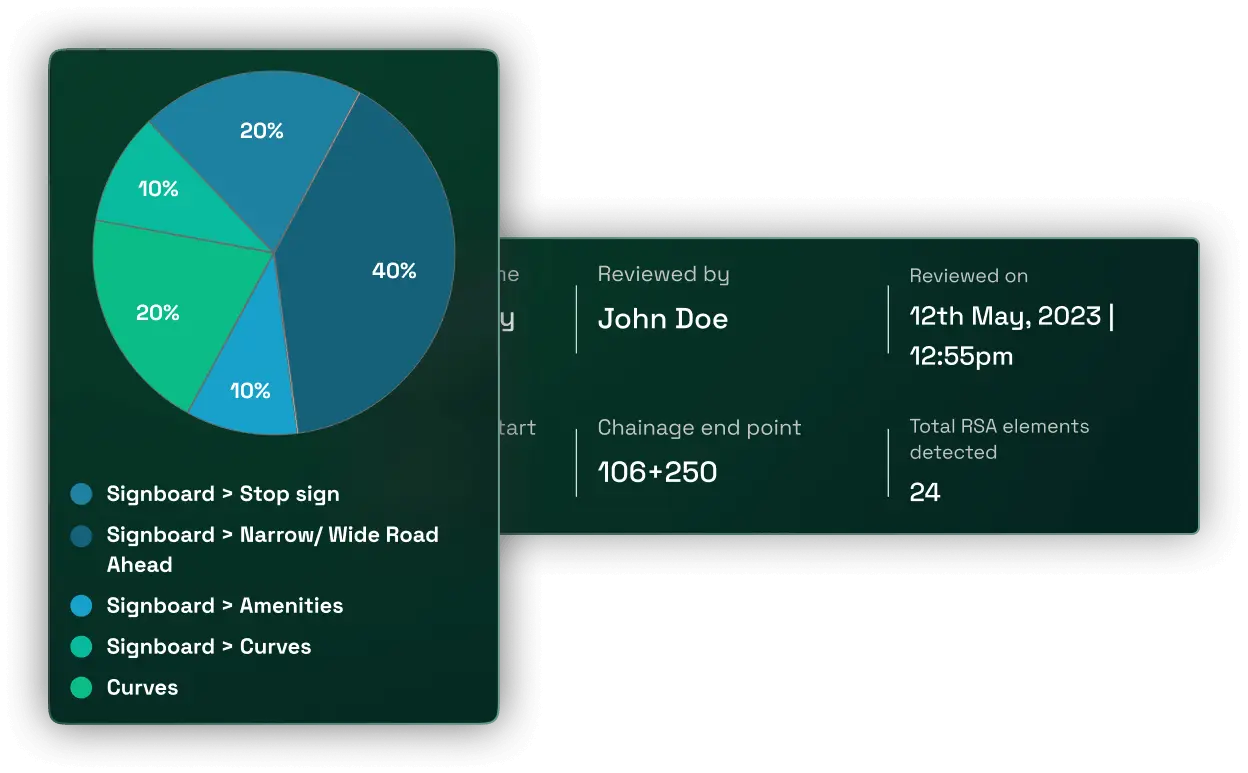
Identification of road safety elements like road markings, signage, lighting, crash barriers, and many more, which need to be improved or added
-
Identification of areas where road markings, signage, lighting, etc. need to be improved or added
-
Identification of areas where enforcement of traffic laws and regulations may need to be increased
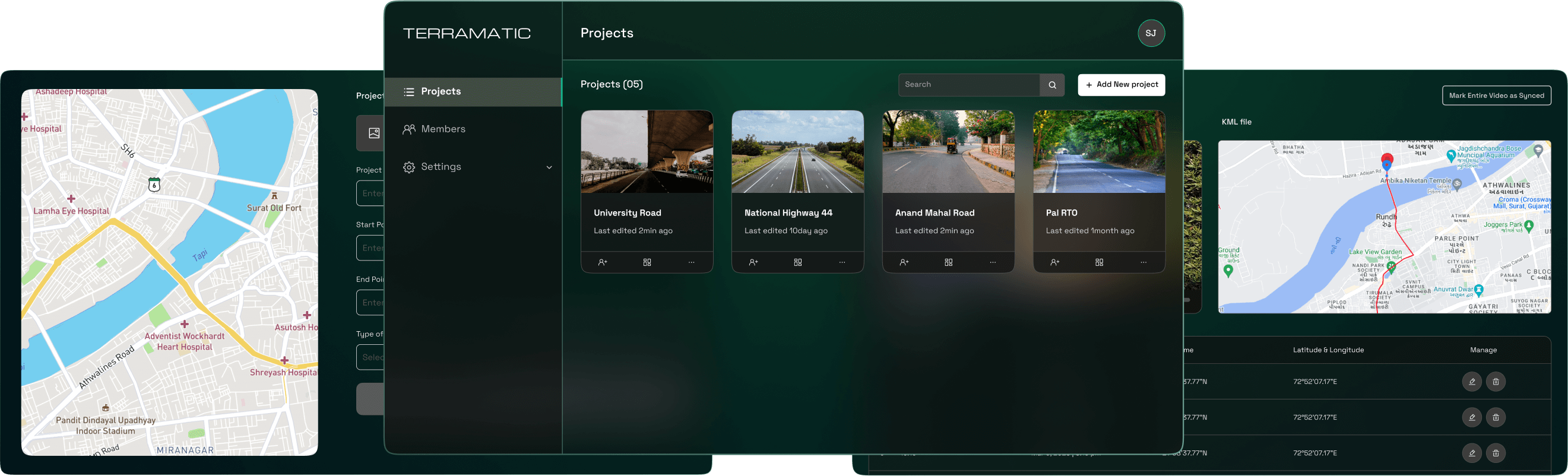
Introducing TERRAMATIC: The key to a more efficient, automated road safety analysis system
Terramatic make Road Safety Audits easier

Identification of potential hazards
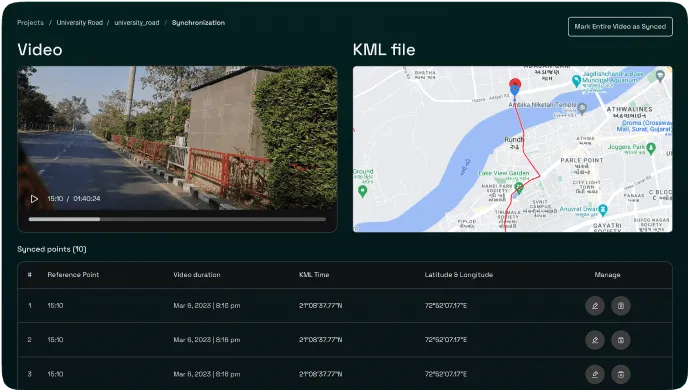
Data analysis of the existing property
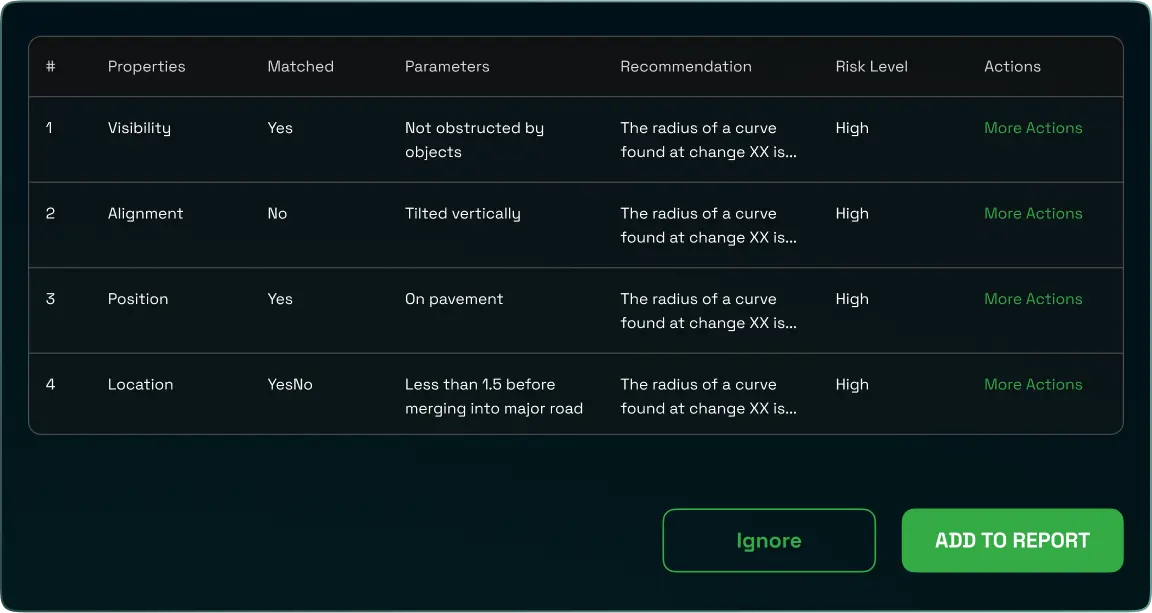
Recommendation Drafting
Implementation
Benefits of using Terramatic


Save time. Increase accuracy. Streamline your road safety audits.
Frequently Asked Questions
A road safety audit is typically required during the planning and design phase of a new road or highway project, as well as during major modifications or upgrades to existing roads. It can also be conducted in response to safety concerns or after a road traffic accident has occurred.
IRC stands for the Indian Roads Congress, which is a professional body that sets standards for the design, construction, and maintenance of roads in India. The IRC has established a number of guidelines and standards for road safety, including the IRC:SP:88-2010 Guidelines for Road Safety Audit, which provides a framework for conducting road safety audits in India.
The principles of road safety audit involve a systematic, proactive, and multidisciplinary approach to identifying potential safety issues and hazards in road design and operation. Key principles include analyzing road user behavior, considering the needs of vulnerable road users, ensuring clear visibility and sightlines, providing appropriate traffic control devices and signage, and ensuring that road design is consistent with the surrounding environment.
The duration of a road safety audit can vary depending on the size and complexity of the project, as well as the level of detail required. A basic road safety audit can typically be completed within a few weeks, while a more comprehensive audit may take several months to complete. It is important to allow sufficient time for the audit to be conducted thoroughly and for any recommended changes to be implemented before the road or highway is opened to traffic.